本文最后更新于 1448 天前,其中的信息可能已经有所发展或是发生改变,请谨慎参考。
捕获异常
try catch关键字
- try:监控类型
- catch:想要捕获的异常,可以捕获异常
- finally:可以处理善后工作,(可以不要finally)
- 使用 try catch关键字可以在出现异常时实现程序不终止,继续跑完程序。我们只需要在try catch中处理这些异常就可以了。
package com.xiheya.exception;
/**
* @Author {xiheya}
* @Date: 2022/03/14/ 9:47
* @Description
*/
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//假设要捕获多个异常:我们要从小到大的去捕获
// 快捷键 Ctrl + Alt + T 快速捕获异常。
try{ //try 监控类型
int a = 1;
int b = 0;
System.out.println(a/b);
}catch (ArithmeticException e){ //catch(想要捕获的异常类型0 捕获异常)
System.out.println("程序出现异常,b不能为0");
}finally { //处理善后工作。可以不要finally,假设IO,资源 关闭
System.out.println("finally");
}
}
}throw 和 throws关键字
- throw关键字一般是在方法体内主动抛出异常
- throws关键字一般是在方法名中抛出异常
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a = 1;
int b = 0;
try {
new Test().test(1,0);
} catch (ArithmeticException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
}
}
public void test (int a , int b)throws ArithmeticException{
if (b == 0){
throw new ArithmeticException();
}
}
}自定义异常
- 使用Java内置的异常类可以描述在编程时出现的大部分异常情况。除此之外,用户还可以自定义异常。用户自定义异常类,只需要继承Exception类即可。
- 在程序中使用自定义异常类,大体可以分为以下几个步骤:
- 创建自定义异常类。
- 在方法中通过throw关键字抛出异常对象。
- 如果在当前抛出异常的方法中处理异常,可以使用try-catch语句捕获并处理;否则在方法的声明处通过throws关键字指明要抛出给方法调用者的异常,继续进行下一步。
- 再出现异常方法的调用者中捕获并处理异常。
代码
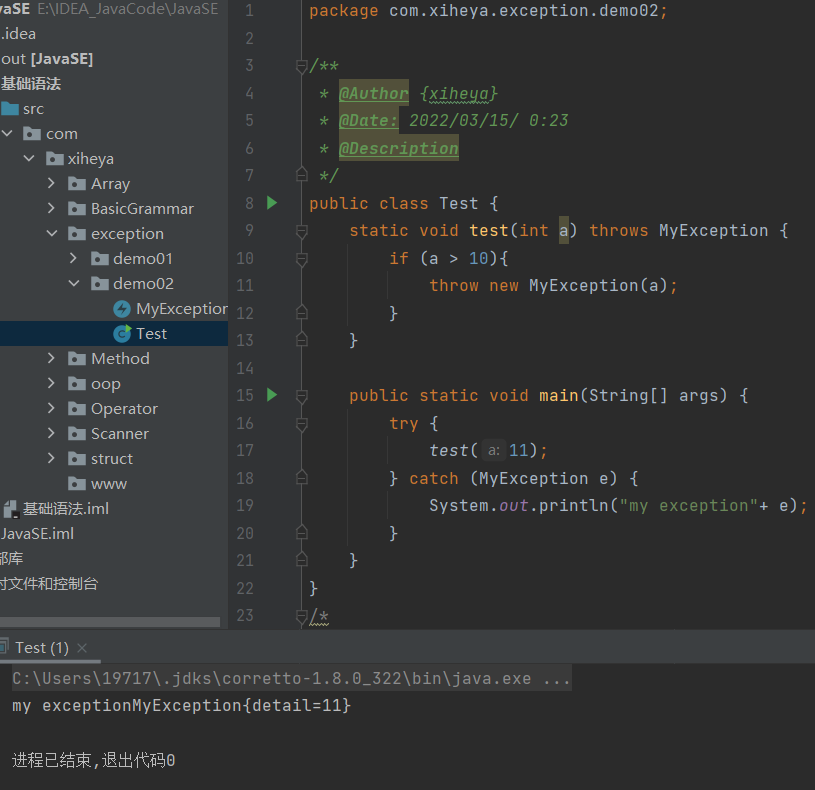
package com.xiheya.exception.demo02;
/**
* @Author {xiheya}
* @Date: 2022/03/15/ 0:23
* @Description
*/
public class Test {
static void test(int a) throws MyException {
if (a > 10){
throw new MyException(a);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
test(11);
} catch (MyException e) {
System.out.println("my exception"+ e);
}
}
}
/*
public class MyException extends Exception{
private int detail;
public MyException(int a) {
this.detail = a;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "MyException{" +
"detail=" + detail +
'}';
}
}
*/运行结果
经验总结
- 处理运行时异常时,采用逻辑去合理规避同时辅助try-catch处理
- 在多重catch块后面,可以加一个catch(Exception)来处理可能会被漏掉的异常。
- 对于不确定的代码,也可以加上一个try-catch,处理潜在的异常。
- 尽量去处理异常,切忌只是简单地调用printStackTrace()去打印输出
- 具体如何处理异常,要根据不同的业务需求和异常类型去决定
- 尽量添加finally语句块去释放占用的资源。







